ThaiHealth takes lessons learned from COVID-19
As Thailand still faces the COVID-19 crisis, ThaiHealth experts recently reconvened to discuss lessons learned from the novel coronavirus and in a bid to better communicate with the public on the outbreak risk and prevention. ThaiHealth summarised the lessons learned the from COVID-19 into the following four chapters:
Chapter 1: The impact of COVID-19 on health promotion and various social dimensions
rn
Chapter 2: ThaiHealth resilience to COVID-19
This chapter provides further details about data collection and SWOT analysis on health crisis management in Thailand during different phases of the outbreak.
Chapter 3: The role of ThaiHealth on implementing health promotion activities during the outbreak period.
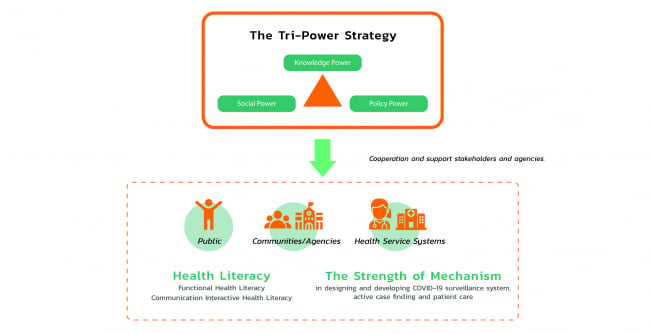
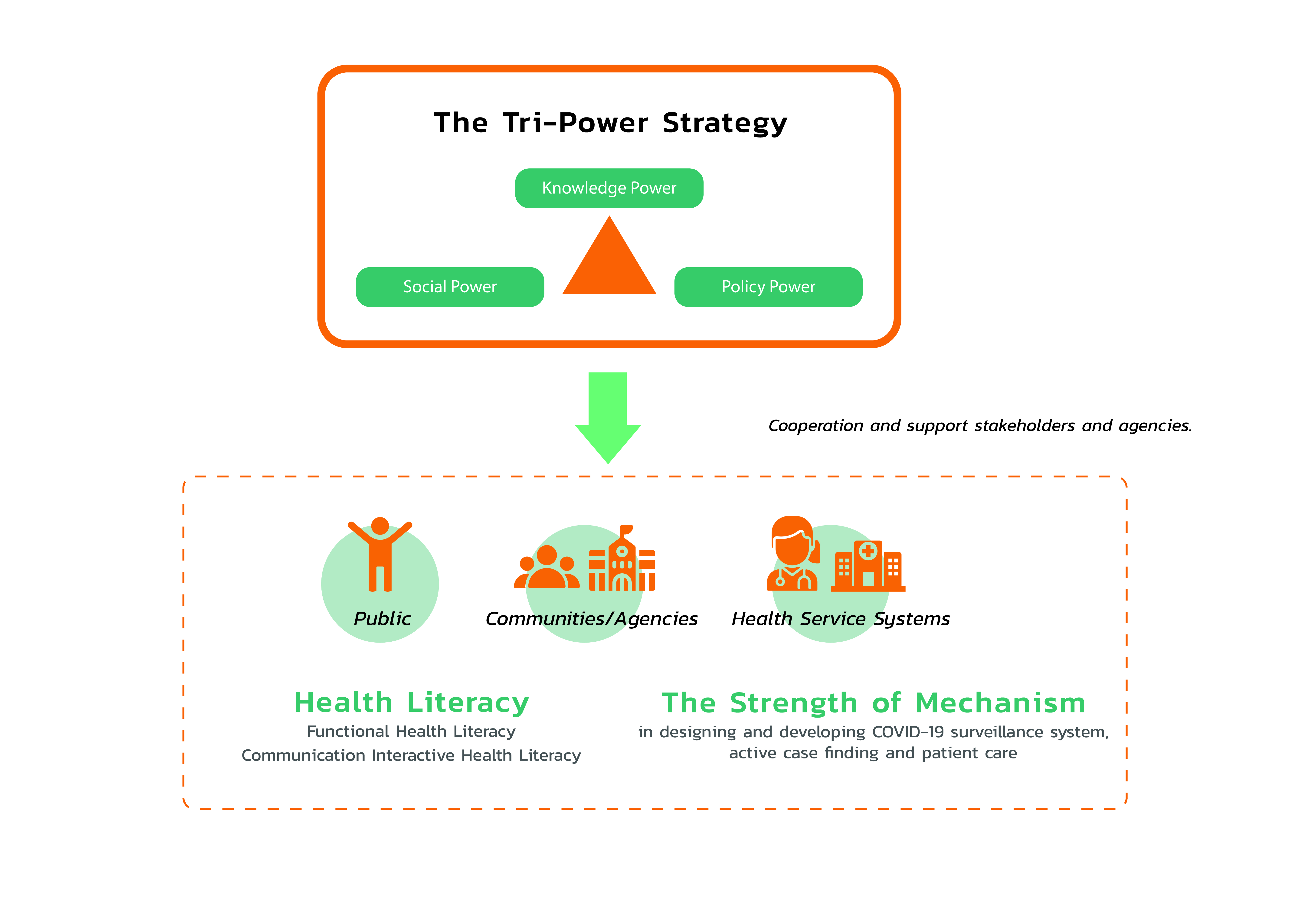
ThaiHealth activities and policy on health promotion implementation can be explained more in depth based on the following three aspects
1. Promote and integrate work within the health policy system. The aim is to ensure that the COVID-19 outbreak prevention can be actively put into practice, leading to cooperation between the area-based panel on living quality development and the National Health Commission Office to drive the so-called “Anti COVID-19 Charter” at the district and the village levels and to develop a model of active COVID-19 case finding in the urban area.
2. Enable community and institute to take part in community surveillance and revitalization to reduce risk of COVID-19 transmission. This includes a development of COVID-19 disease surveillance by the community, safe and COVID-19 free fresh market, and lesson learned to tackle COVID-19 outbreak.
3. Develop a health communication system which is accessible for the target group, and beneficial for developing knowledge management mechanism to communicate with not only the Ministry of Public Health but also the public. The “Fighting COVID-19” series of communications tools comprising Infographic posts with simple, reader-friendly and suitable messages is the evident output aimed at communicating COVID-19 risk of transmission at different locations for example private residences, condominium, apartment, dormitory, office building, public transportation, school, nursery, temples etc. with different groups including ethnic minorities, LGBTIs, and transnational population. A news fact-checking model should also be available so that the public can identifyfacts and fake news.
Chapter 4: Health promotion for reducing the impact of any unforeseen communicable disease outbreak
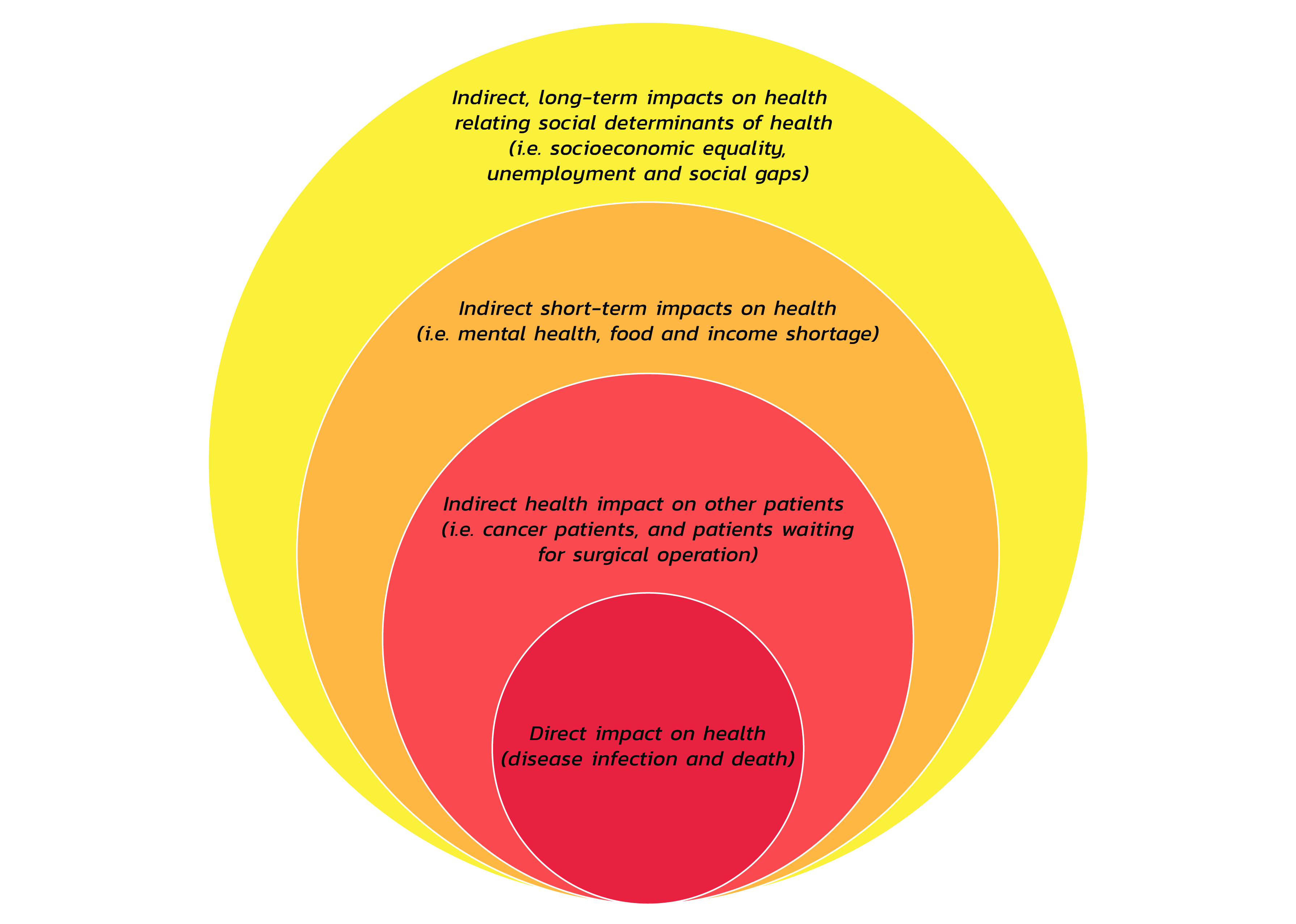
This chapter explains details about sustainability and related social determinants of health including deaths, illness, life expectancy, expenses on health services, health status, health system effectiveness and limitations. The COVID-19 outbreak reflects the negative impact of outbreak on all social determinants, resulting in social and later health instability.
One of the key lessons learned from the COVID-19 crisis is that public immunity should be integrated into the health surveillance preparation for the next phase of disease outbreak apart from the existing medical and public health aspect. This solution will help enhance resilience, and strengthen social determinants of health, leading to the new normal life in action at the personal, social and health system levels. Thailand will also be able to cope with the indirect impact of COVID-19 on health in the long run.

rn





